
The phonetics and phonology difference can be explained by their approaches and methods as a science.
Phonics is a method of teaching to read when each letter is pronounced as in the alphabet. Hence, this science is a branch of linguistics. Phonetics is the academic study of the sounds of a language.
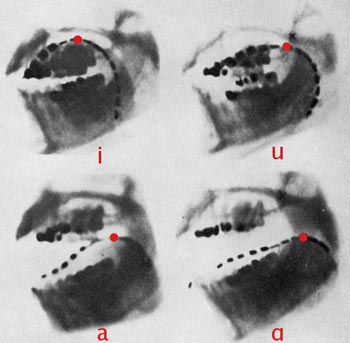
Sometimes the meaning of phonics is limited to a simplified definition of phonetics. Most ESL textbooks explain these components using the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) which is described below.

To make it simple, it describes the way we produce and perceive the sounds of speech. For this reason many students will "hear" /tʃ/ in words like orange or judge.The English phonetic system comprises the four components: speech sounds, syllabic word structure, stress, and intonation. The sound of these letters is never in final position. In Spanish the letters "ll" and "y" sound similar to /dʒ/, /ʒ/ or /j/.

For example, the pronunciation of "nutshell" is /ˈnʌt.ʃel/ and "nature" is pronounced /ˈneɪ.t͡ʃər/.Īnticipated pronunciation difficulties depending on L1 Spanish t/ and /ʃ/ can be two separate phonemes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
